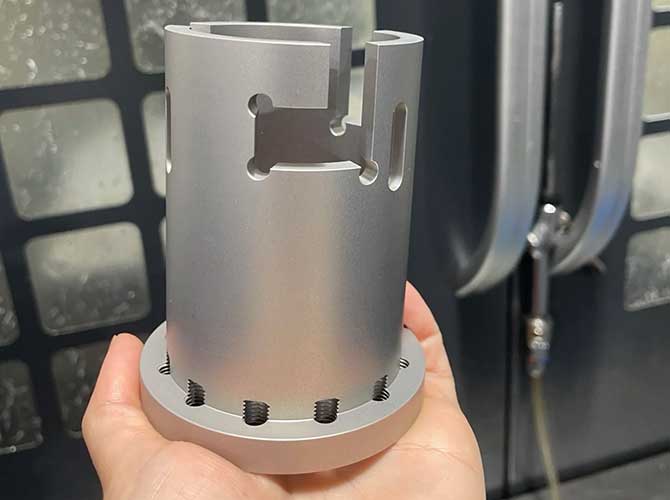
Precision is at the heart of CNC machining and designing with the right tolerances can make or break your project. Get it wrong, and the parts might not fit or function.
Effective CNC machining tolerances are crucial for ensuring parts meet specified dimensions, fit together seamlessly, and function as intended without unnecessary costs.
Getting tolerances right ensures that the parts come out as expected and fit perfectly in assemblies. Ahead, we'll delve into the specifics of designing tolerances.
What are CNC Machining Tolerances and Why are They Important?
Precision is everything in CNC machining; understanding tolerances is key to achieving it. Yet, it often remains a complex aspect for many designers.
CNC machining tolerances define permissible limits of variation in part dimensions, ensuring correct fit and function while managing costs effectively.
Tolerances ensure that parts manufactured through CNC machining fit and function properly. They indicate allowable deviations from a specified dimension. Too tight tolerances increase costs and lead times due to prolonged machining processes, while too loose ones may result in components that don’t fit or operate correctly. By clearly defining tolerances, you ensure that the final product meets quality standards without unnecessary expenditure.
What Factors Influence Tolerance Selection in CNC Machining?
Selecting the right tolerance involves balancing precision with cost and material capabilities. Mistakes here can cascade into production issues.
Factors influencing tolerance selection include material properties, part function, production volume, and cost considerations, balancing precision with practicality.
When deciding on tolerances, consider the material's properties and how they may affect manufacturing. For example, metals might require different tolerances than plastics. The function of the part is another critical aspect: moving parts might need tighter tolerances. Production volume also affects this choice. High volumes might justify tighter tolerances’ costs, while limited runs might not. Practicality lies in finding a balance between precision needs and cost constraints.
How Do Tolerances Affect CNC Machining Costs?
Cost overruns are a common pitfall in CNC machining projects. Tolerances play a major role in this area.
Tighter tolerances often increase CNC machining costs due to necessity for slower, more precise machining processes and additional quality control measures.
Implementing tight tolerances can significantly drive up costs. Achieving minute precision requires extended machining times, careful handling, and sometimes even specialized equipment. Each of these factors contributes to longer production times and higher financial outlay. Additionally, tight tolerances can lead to higher rejection rates during quality control. Thus, ensuring your tolerance specifications are realistic and necessary for the part’s function helps keep costs manageable.
Are There Standard Tolerances in CNC Machining?
Standard tolerances serve as a guideline for manufacturers. However, knowing when to deviate from them is vital for specific needs.
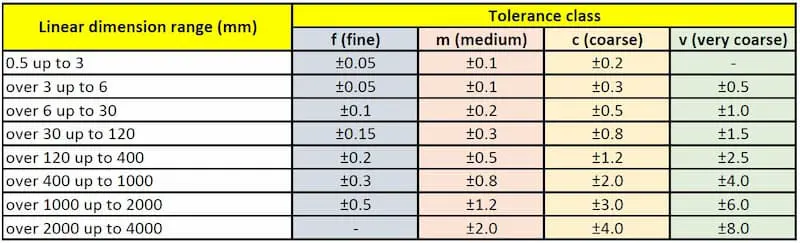
Standard CNC machining tolerances typically range from ±0.005 to ±0.01 inches, offering a baseline for most general machining applications.
Standard tolerances provide a foundation, but actual tolerance decisions should align with the specific application needs. For general purposes, a tolerance of ±0.005 to ±0.01 inches is often used. However, certain industries, like aerospace or medical, may require much tighter specifications. Always consult with your manufacturing partner to ensure the chosen tolerances align with your project's performance requirements and cost constraints.
Conclusion
Designing effective CNC machining tolerances requires balancing precision, cost, and material capabilities to ensure components meet functional needs without unnecessary expenditure.