I often wondered, how frequent should inspections be during CNC machining to avoid costly mistakes without slowing down production?
The inspection frequency depends mainly on the complexity and processing time of the product. Complex parts with long machining times require longer inspection intervals, while simple products should be inspected every 30 minutes to ensure quality.
Balancing inspection frequency is key to keeping production smooth and products error-free. Too few checks risk flaws slipping through, and too many can slow down the workflow. Let's explore what CNC inspections are, how often to inspect access equipment, what daily maintenance keeps machines running smoothly, and the safety measures to stay safe during CNC processes. Stopping now risks missing the core steps to improve your CNC workflow.
What is CNC inspection?
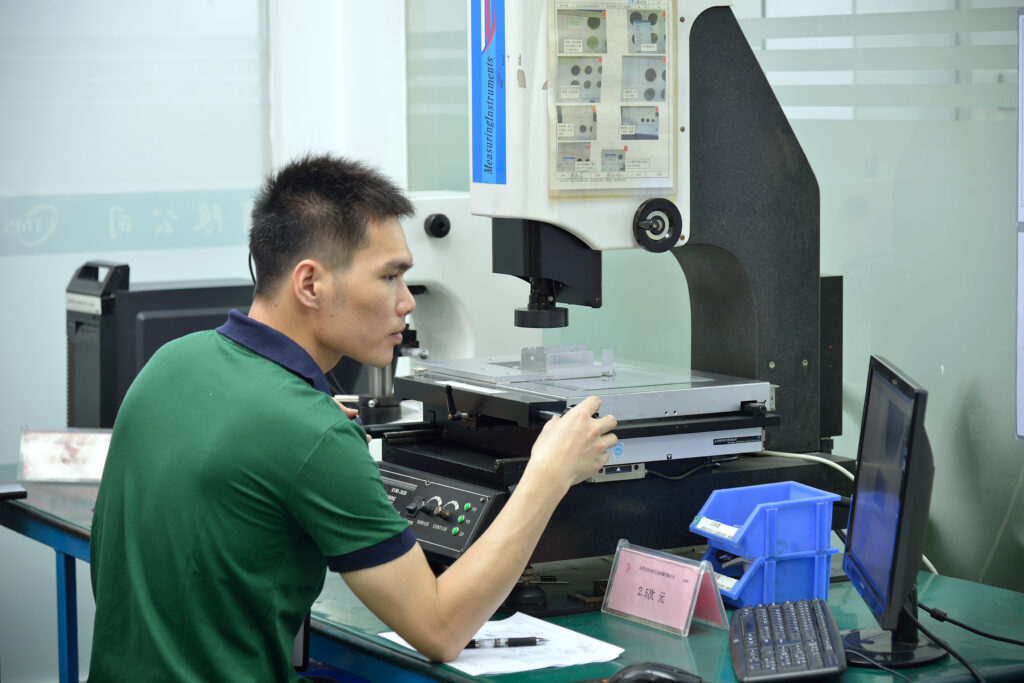
CNC inspection means checking parts and processes at various stages to ensure quality standards are met.
It is a process of examining machined parts or CNC setups periodically using measurement tools and visual checks to detect defects early.
CNC inspection involves measuring dimensions, surface finishes, and geometry using calipers, micrometers, or CMM (coordinate measuring machines). It also includes reviewing machine settings and tool conditions. Inspections catch errors caused by tool wear, machine calibration issues, or operator mistakes before large batches are produced. Using standard inspection protocols tailored to the product complexity improves yield and reduces costly reworks.
| Inspection Type | Purpose | When to Perform |
|---|---|---|
| In-process inspection | Detect issues during machining | At set intervals based on product complexity |
| Final inspection | Confirm product meets specs before shipping | After machining completion |
| Tool condition check | Prevent quality loss from tool wear | Regularly during production |
Proper inspection acts like a safety net, catching problems early to save time and money.
How often should you inspect access equipment?
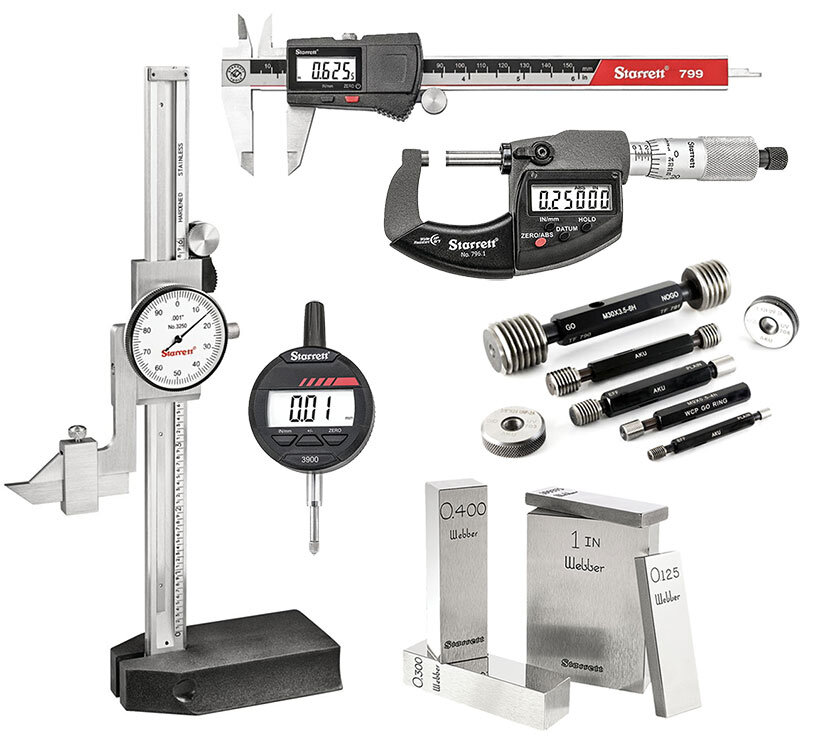
I learned that inspecting access equipment like jigs, fixtures, and measuring tools must be regular to keep CNC parts precise.
Inspect access equipment daily for wear or damage; tool calibration should be checked before each shift to ensure accurate machining.
Keeping equipment in top shape is crucial because faulty jigs or uncalibrated tools can lead to incorrect parts. The inspection frequency depends on machine workload and product complexity. For high-volume or critical components, inspecting every hour or between batches pays off. For simpler runs, daily checks before starting work protect against surprises.
Using a checklist helps standardize inspections and quickly spot problems. It also reminds operators how important precise fixtures and tools are for quality outcomes.
| Equipment Type | Inspection Frequency | Key Checks |
|---|---|---|
| Fixtures and Jigs | Daily or between batches | Wear, alignment, cleanliness |
| Measuring Tools | Before each shift or use | Calibration, damage, accuracy |
| CNC Accessories | Weekly or per manufacturer’s recommendation | Functionality and cleanliness |
Consistent access equipment inspection supports stable machining results and reduces downtime.
What is the daily preventive maintenance checklist for CNC machines?
Skipping daily maintenance often leads to breakdowns and reduced machine lifespan.
Daily preventive maintenance includes cleaning, lubricating, checking coolant levels, and inspecting critical components for wear or damage.
A typical daily checklist might look like this:
| Task | Details |
|---|---|
| Clean machine surfaces | Remove chips, dust, and debris |
| Lubricate moving parts | Apply grease or oil to spindles, guides |
| Check coolant levels | Maintain proper coolant concentration |
| Inspect tool holders and spindles | Look for wear, tightness, or cracks |
| Test emergency stops | Confirm safety mechanisms function correctly |
These steps help avoid unexpected failures and keep the CNC running accurately. I always recommend operators perform these checks before starting work to catch any early signs of trouble. Regular lubrication also prevents wear and machine corrosion.
Adding maintenance tasks into daily routines saves time and reduces costly repairs later.
What safety precautions should be observed during a CNC process?
Safety is always a priority in CNC machining to protect operators from hazards.
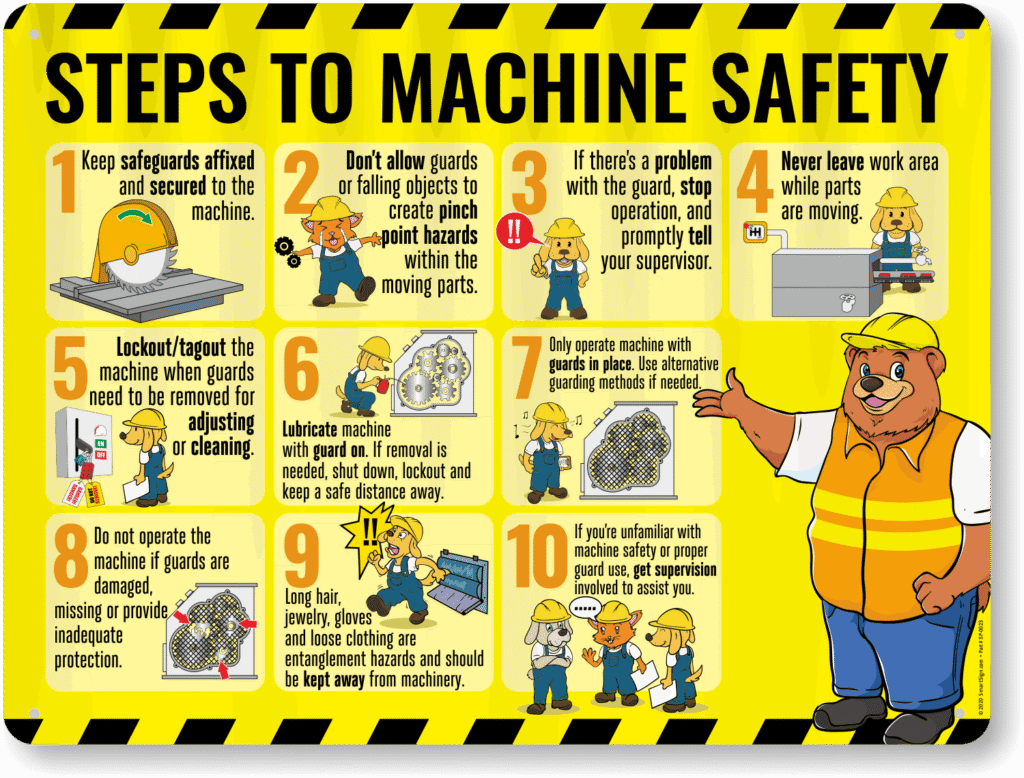
Wear personal protective equipment, keep work areas clean, follow lockout/tagout procedures, and never bypass machine safety guards.
Some common safe practices include:
- Wearing safety glasses and ear protection
- Removing loose clothing and tying back long hair
- Ensuring emergency stops are accessible
- Keeping flammable materials away from machines
- Using proper ventilation to reduce fumes or dust
Safety rules prevent accidents that not only hurt people but halt production. Training operators on machine use, hazards, and safe behaviors is key. Regular safety audits and clear signage remind everyone to maintain safe environments.
| Safety Precaution | Reason |
|---|---|
| PPE (glasses, gloves) | Protect eyes, skin, and hands |
| Clean workspace | Prevent slips, trips, and fires |
| Lockout/tagout | Avoid accidental machine starts |
| Machine guards | Shield operators from moving parts |
| Training and signage | Reinforce safe practices |
Following these simple safety steps keeps the workplace secure and efficient.
Conclusion
Customizing inspection intervals by product complexity, combined with regular equipment checks, preventive maintenance, and safety, optimizes CNC processes and protects quality.