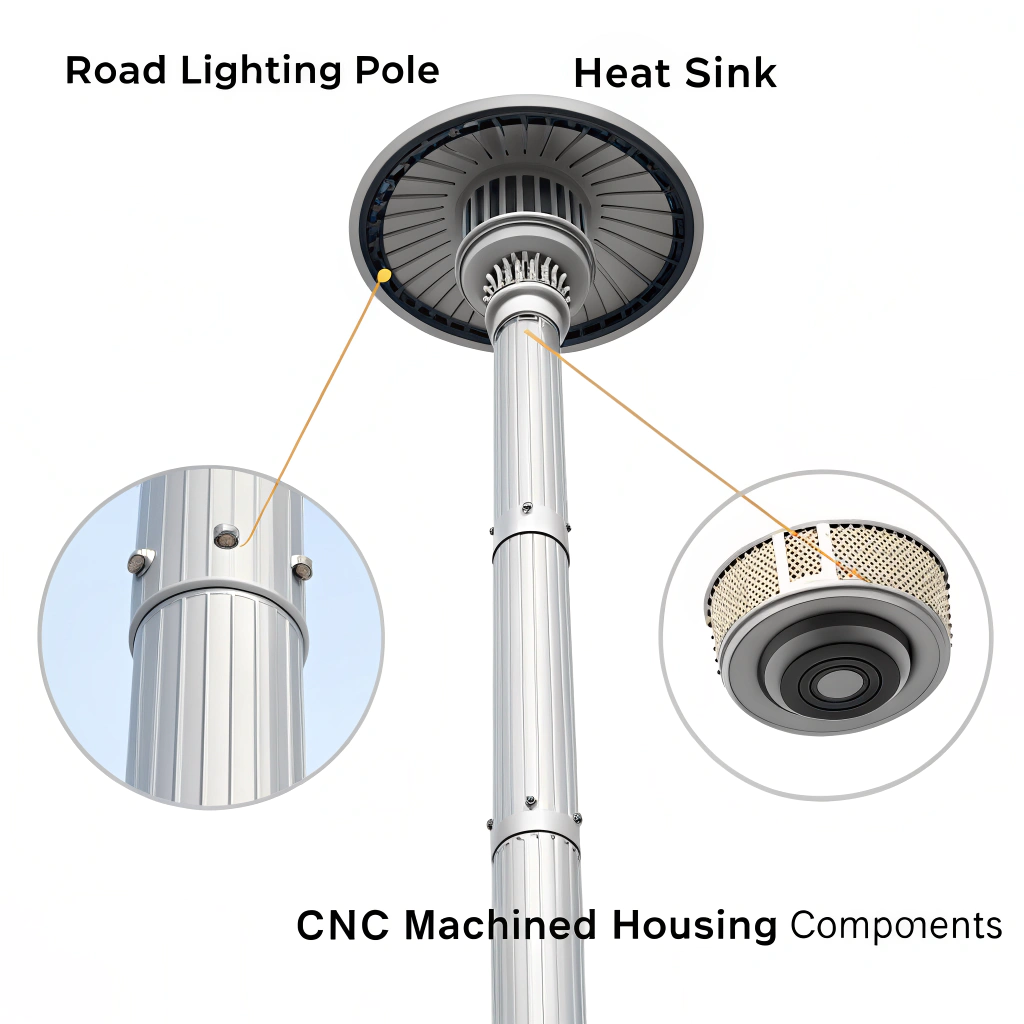
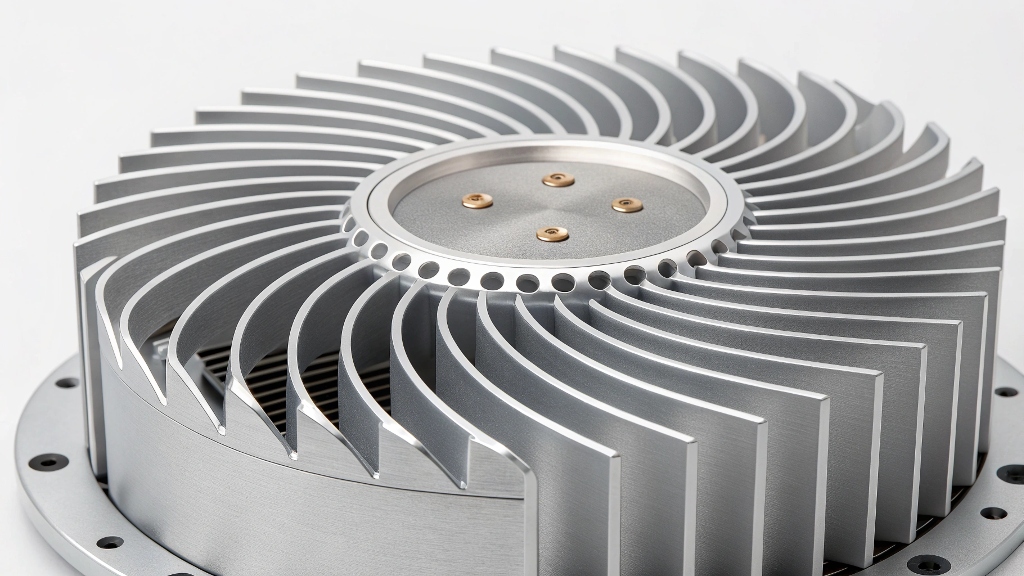
Precision machining is crucial in addressing the common issue of heat distortion in high-power lamps. Heat distortion can lead to inefficient performance and potential failure of the product.
Precision machining reduces heat distortion in high-power lamps by ensuring accurate component alignment and optimal thermal management. It minimizes gaps and inconsistencies that can lead to overheating and material deformation.
Precision machining offers significant benefits, but understanding how it works can enhance its application. Let's dive deeper into how it impacts high-power lamps.
What Causes Heat Distortion in Lamps?
Lamps endure heat due to high power output, and this can warp materials over time. Material warping can lead to poor performance and decreased lifespan of the lamps.
Heat distortion in lamps is caused by inefficient heat dispersion and inconsistent material structures. Excessive heat in concentrated areas leads to deformation, affecting the lamp's functional integrity.
Understanding the primary causes of heat distortion is vital. Material choice plays a key role; metals need to withstand high temperatures. Coupled with precision machining, this ensures consistent material structure, minimizing distortion. Aligning components precisely and using quality materials not only prevents heat-related issues but also enhances performance longevity. By targeting the root causes, we can improve lamp efficiency and durability.
How Does Precision Machining Improve Component Alignment?
Misalignment can lead to uneven heat distribution, causing parts to warp or degrade. Once weakened, these parts may compromise lamp functionality.
Precision machining improves alignment by creating uniform parts that fit together seamlessly. This results in even heat distribution, minimizing the risk of distortion or degradation.
The precision used in machining plays a vital role in maintaining component stability. When parts fit together perfectly, it ensures that heat disperses evenly. Aided by technologies like CNC machining, dimensions are controlled tightly. This helps in maintaining consistency across production batches, reducing errors, and leading to higher product quality. A well-aligned assembly faces less stress, securing the longevity and effectiveness of high-power lamps.
Why is Material Selection Important for Heat Management?
Selecting the right materials ensures efficient heat management. Materials that cannot handle high heat lead to increased wear and distortion.
Material selection is key to heat management. High conductivity metals like aluminum or copper allow for better heat dissipation, reducing heat buildup and distortion.
Choosing the right materials is about balancing conductivity and cost. Metals with high thermal conductivity help in swiftly dispersing heat away from vulnerable parts. This prevents localized hotspots from forming. Meanwhile, the right coating can also aid in reflecting excess heat. But it's not just about heat; the material must also provide structural support. Thus, incorporating optimal materials contributes to both the functional efficiency and longevity of high-power lamps.
What Are the Long-Term Benefits of Using Precision Machining?
While initial costs may seem high, the long-term advantages justify the investment. Precision machining ensures reliable performance and fewer replacements.
Precision machining offers long-term benefits like enhanced durability, reduced maintenance, and increased efficiency, leading to better overall value for high-power lamps.
In the long run, precision machining pays off by reducing the frequency of flaws and avoiding costly repairs. The stable performance of high-power lamps ensures they operate effectively under high temperatures without unexpected failures. As components fit perfectly, the consistent quality reduces waste. This approach secures a higher return on investment by minimizing downtime and maintenance costs. Thus, a one-time investment in precision machining transforms into sustained performance and reliability.
Conclusion
Precision machining is essential for reducing heat distortion in high-power lamps, improving efficiency, longevity, and performance through optimal component alignment and material selection.