Maximizing quality while minimizing costs can feel overwhelming in CNC machining. What strategies can help achieve this balance without compromising on excellence?
Reducing the cost of CNC machined parts without sacrificing quality involves efficient design, selecting appropriate materials, and optimizing the machining process. Strategic decision-making can cut expenses while maintaining high standards.
Balancing cost and quality in CNC machining starts with optimization. Streamlining the process ensures high-quality outputs without unnecessary expenditure.
What Role Does Design Play in Cost Reduction?
Design is the blueprint of cost-effectiveness. Can thoughtful design decisions directly influence costs and quality in CNC machining?
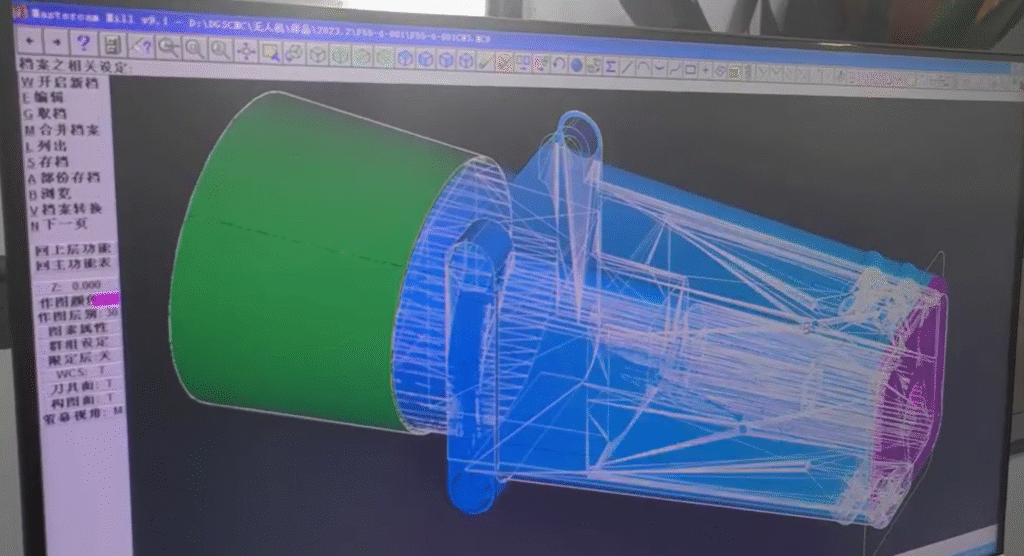
Design plays a pivotal role in cost reduction by simplifying geometry, minimizing complex features, and ensuring ease of manufacture—leading to efficient and low-cost production without quality compromise.
Simple designs with fewer intricate details reduce machining time and tool wear. Complex shapes often require additional tool changes and longer production times, elevating costs. Designers should collaborate closely with machinists to ensure designs are feasible and efficient for production. Moreover, using standard dimensions and tolerances can streamline the process. This practice minimizes setup time and material waste, leading to cost savings. By anticipating manufacturing challenges early in the design phase, issues requiring costly corrections later can be avoided, ensuring both affordability and quality.
How Does Material Selection Impact Costs?
Materials form the backbone of any CNC project. How can choosing the right material effectively reduce costs without compromising performance?
Material selection impacts costs by balancing price with performance. Choosing materials that are easy to machine and fit the product's functional requirements can lower expenses while maintaining excellence.
In CNC machining, materials range from soft plastics to hard metals. Soft materials often machine faster and require less power, reducing overall costs. However, the material’s properties must align with the product’s requirements. A careful assessment of the necessary mechanical, thermal, and chemical properties will guide optimal material choice. Sourcing materials readily available locally can also diminish costs associated with transportation and storage. Selecting materials that provide the best trade-off between machinability and performance can yield significant savings and maintain product quality.
What Machining Process Optimizations Can Lower Costs?
The machining process can be resource-intensive. What adjustments can streamline operations and cut costs effectively?
Machining process optimizations, including reducing setup time, using efficient cutting strategies, and implementing preventive maintenance, can substantially lower costs while ensuring quality CNC machined parts.
Reducing machine setup and transition times contributes significantly to cost efficiency. This involves planning production runs to minimize machine downtime. Utilizing advanced cutting strategies, such as high-speed machining or adaptive machining paths, can enhance material removal rates and reduce cycle times. Regular maintenance ensures machines operate at peak efficiency, preventing costly downtime. Additionally, investing in skilled programmers and operators can optimize tool paths and minimize material waste. These strategic cues enhance process efficiency, yielding cost-effective yet high-quality results.
How Can Volume and Batch Size Affect Costs?
Manufacturing volume dictates scale and expense. How can adjusting volume and batch size impact cost-effectiveness in CNC machining?
Volume and batch size affect costs as larger production runs lower unit costs due to economies of scale, making CNC machining more cost-effective for bulk orders.
Producing in larger quantities generally distributes fixed setup costs across a greater number of units, reducing the cost per part. Achieving an optimal batch size ensures production efficiency without overproducing. However, the decision to ramp up production volume should consider demand forecasts and storage capabilities to avoid overproduction and increased inventory costs. Collaborating with suppliers on bulk material purchases can lead to discounts, further reducing expenses. Adjusting volume and batch size strategically can save costs while fulfilling quality standards.
Conclusion
Efficient design, material selection, and process optimizations lead to cost-effective, high-quality CNC parts, balancing economy with performance successfully.