Creating the perfect metal component can be challenging, but understanding when to prototype and when to move into mass production is crucial. This decision affects the cost, timeline, and overall success of the project.
Prototyping allows for testing and refinement of designs before full-scale production. Mass production focuses on efficient, large-scale replication of finalized designs using CNC technology.
Navigating the transition between prototyping and mass production in CNC services can be confusing. Knowing when to prototype maximizes design efficiency while moving to mass production ensures scaled output—each phase calls for distinct strategies.
Why is prototyping essential for CNC projects?
Prototyping identifies design flaws and verifies functionality, reducing costly revisions later. It's the testing ground for innovations without committing resources prematurely.
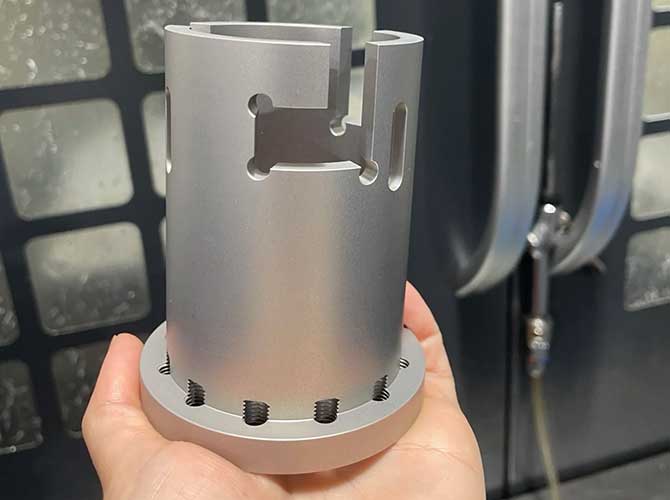
Prototyping involves creating a small batch to test design integrity. It’s critical for ensuring design accuracy and functionality before mass production, minimizing costly errors later.
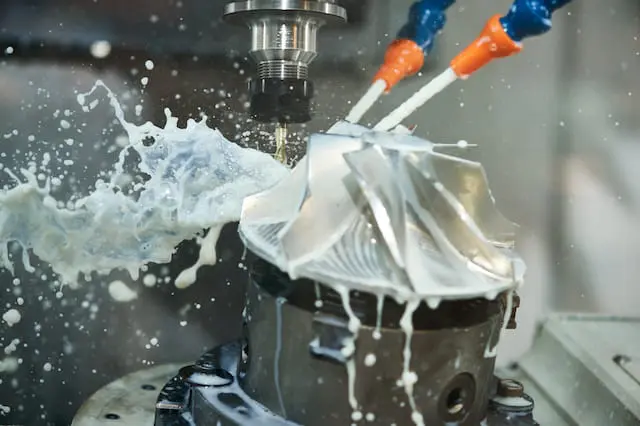
When starting a CNC project, initiating with a prototype helps piece out design possibilities and constraints. This phase allows developers to test materials, mechanics, and aesthetics. CNC prototyping can uncover potential issues or improvements, ensuring the final product meets expectations. With CNC technology, modifications and adjustments become an agile process—refining designs before committing to full-scale production.
How does mass production optimize CNC efficiency?
Mass production in CNC guarantees consistency, cost-efficiency, and scalability. It’s about producing uniform parts quickly and reliably.
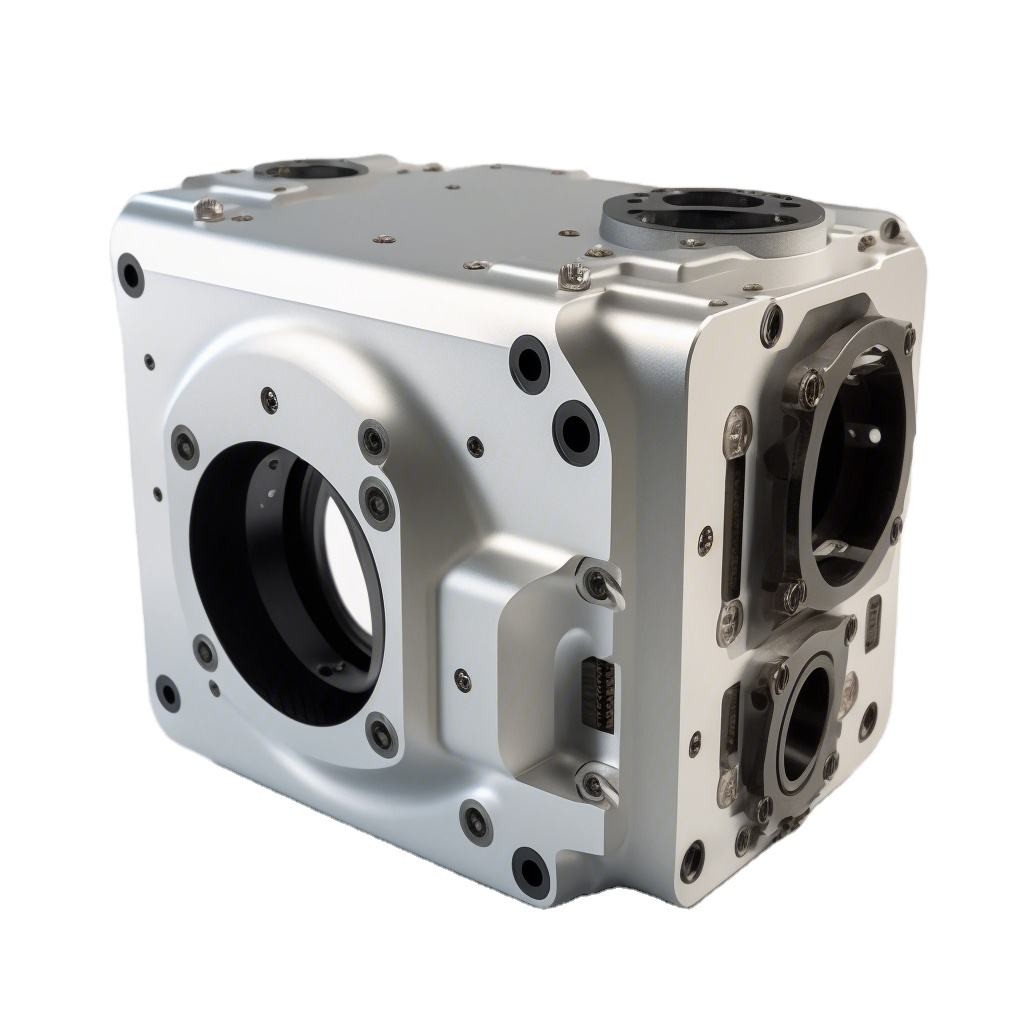
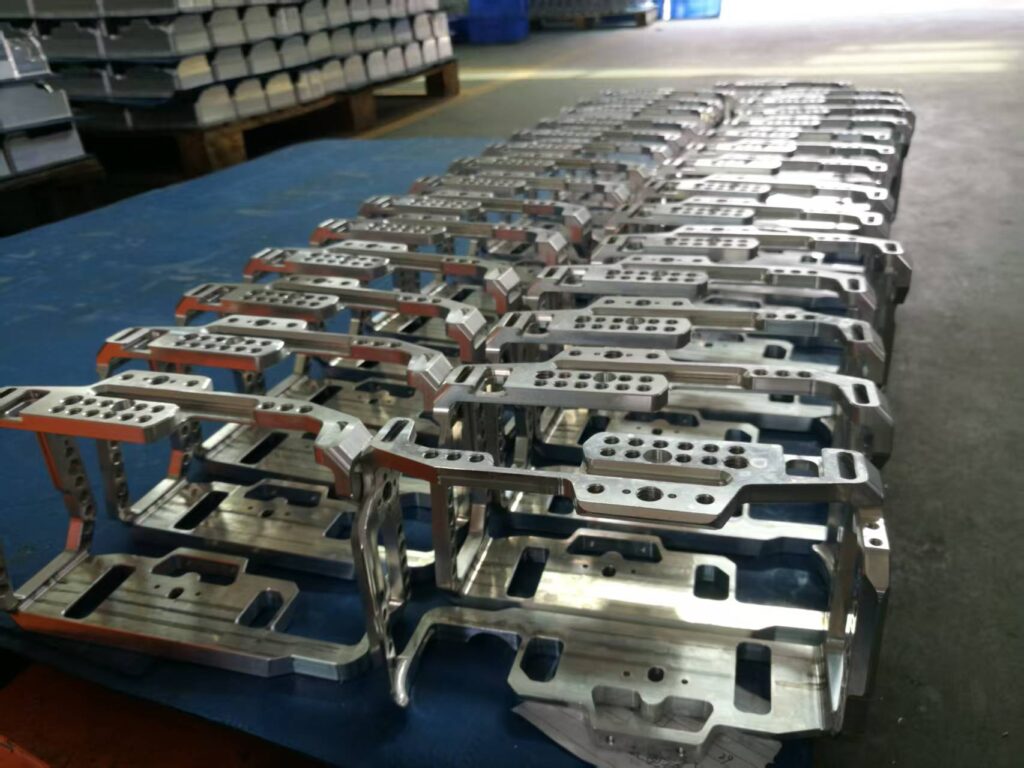
Mass production uses established CNC processes to create large quantities of precise parts, enhancing efficiency while reducing unit costs and maintaining high quality.
Once a prototype is refined, transitioning to mass production is seamless with CNC technology. By using automation and precision machining, manufacturers can produce large volumes of components efficiently. The emphasis lies in maximizing throughput while maintaining strict quality standards, ensuring each piece adheres to original design specifications. CNC mass production supports scalability—easily adjusting for higher output demands while ensuring budget compliance and time efficiency.
How do we tailor CNC services to meet diverse needs?
Understanding client-specific requirements helps customize CNC strategies—prototyping involves creating custom designs, while mass production focuses on reproducing perfected models.
Tailoring involves adapting CNC methods to fit project goals, from initial design creation in prototyping to structured replication in mass production, ensuring alignment with client objectives.
Customization is key to meeting varied project goals within CNC services. During the prototyping phase, unique designs and material choices are explored and adjusted based on feedback and testing. On transitioning to mass production, standardizing processes ensures efficient scalability without compromising quality. Our approach involves collaboration with clients, precisely tailoring CNC techniques to suit their product, budget, and timeline needs. We aim to align every phase with project success, embracing flexibility and innovation.
Conclusion
Choose prototyping for design refinement, and mass production for efficiency and consistency—each phase aligns with your specific CNC project needs.