The efficiency of electronics depends on heat management—but which industries rely most on heat sinks?
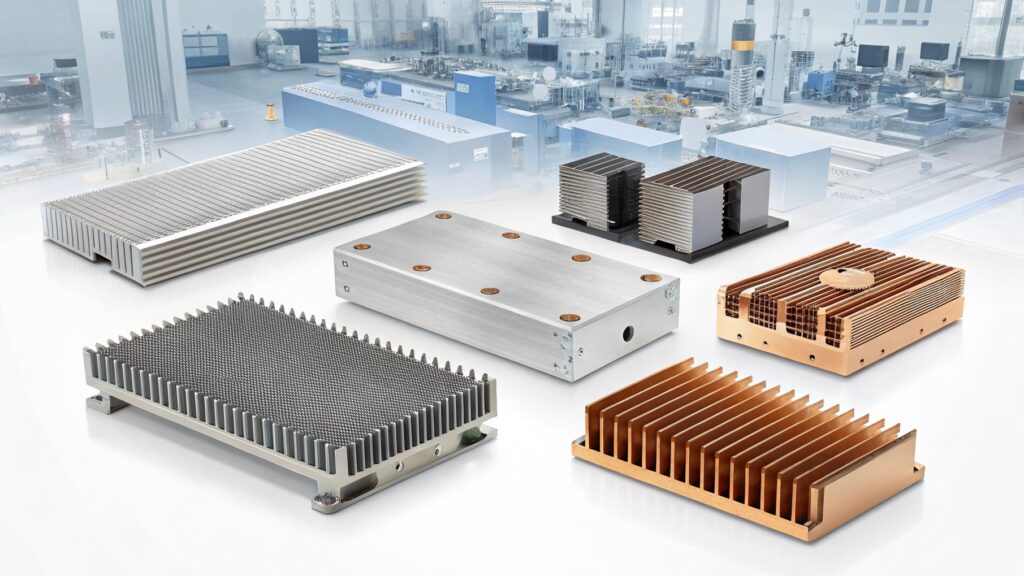
Heat sinks are vital in industries like consumer electronics, telecommunications, automotive, and gaming, providing essential cooling for devices ranging from computers to 5G stations.
Electronics are everywhere; from laptops to cars, they need proper cooling systems. We must explore how various industries utilize these essential components.
What is a heat sink mostly used in?
Heat management is crucial. But what sectors rely on heat sinks the most?
Heat sinks are primarily used in sectors like consumer electronics, automotive, telecommunications, and IT to prevent overheating and ensure efficiency.
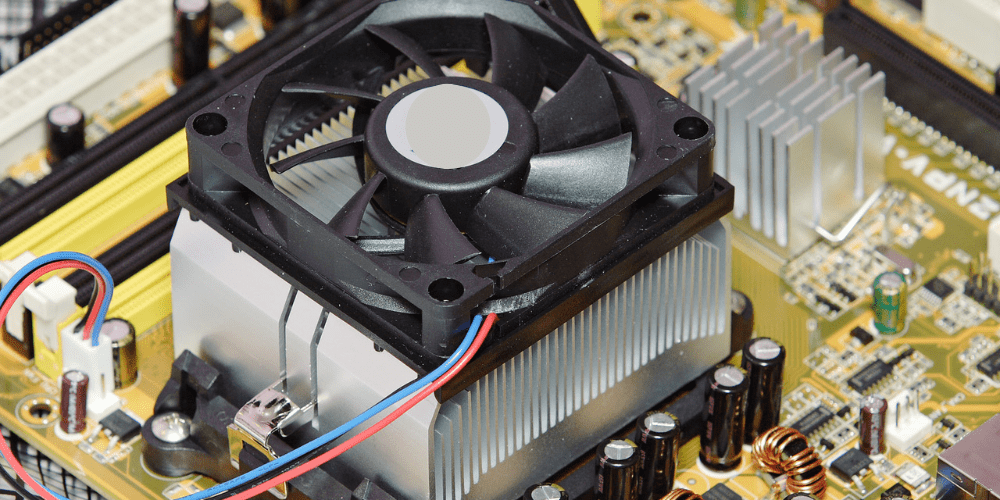
Heat sinks are integral to electronic devices, acting as vital cooling agents. They dissipate heat from microprocessors, ensuring devices run smoothly and safely. In consumer electronics, they are present in computers, video game systems, and mobile devices. The automotive industry uses them in electric vehicle components. Telecommunications rely on heat sinks within 5G service stations and servers, where heat output is significant. The IT industry also uses them in data centers to ensure non-stop operations.
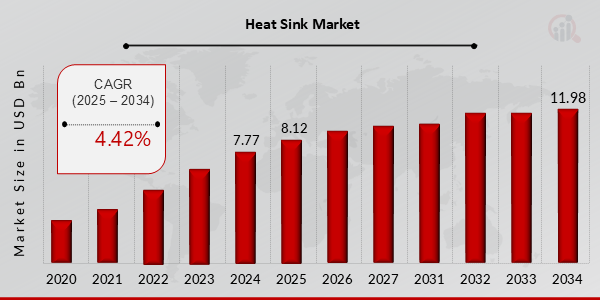
How big is the heat sink market?
Curious about the size of the heat sink market? Let's analyze its scope.
The heat sink market is substantial and growing, driven by demand in consumer electronics, telecommunications, automotive sectors, and renewable energy systems.
As technology advances and becomes more prevalent, the need for efficient cooling solutions rises. Industry reports estimate significant growth in the heat sink market in the coming years, fueled by innovations in electronics and expansion in sectors like renewable energy. Companies are investing in research and design to create more efficient models. The surge in electric vehicles and telecommunication equipment further supports market expansion. This growth is closely tied to the development of materials and techniques that enhance heat sink effectiveness.
When to use a heat sink?
Timing is key in deploying heat sinks in electronics. But when exactly are they essential?
Use heat sinks when electronic components generate excess heat that could cause damage or inefficiency, such as in high-performance processors and power transistors.
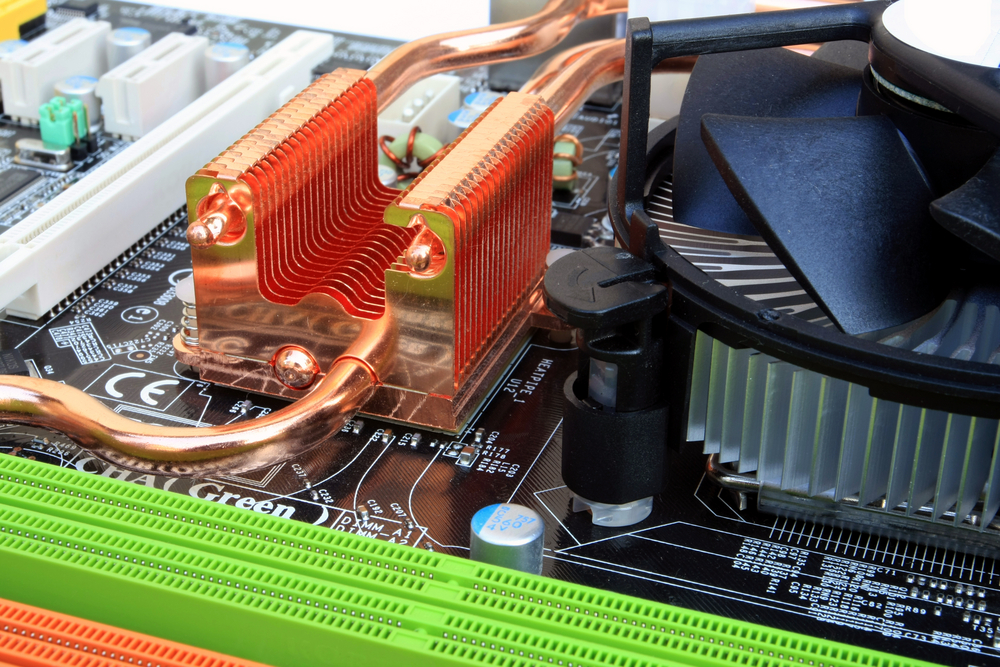
In electronics, heat can affect functionality and lead to failure. Heat sinks are critical in situations where devices operate under heavy loads or in high-temperature environments. They maintain optimal performance by dissipating heat from components like CPUs, GPUs, and LED lights. In tech infrastructure, such as data centers, preventing overheating is paramount for reliability. Consider using heat sinks in equipment that undergoes intensive processes like gaming consoles, servers, and automotive electronics. This ensures durability and longevity, preserving device health and efficiency.
Which industry uses plate heat exchangers?
Plate heat exchangers are common, but which industries benefit most from them?
Industries like HVAC, chemical processing, food and beverage, and refrigeration extensively use plate heat exchangers for efficient thermal management.
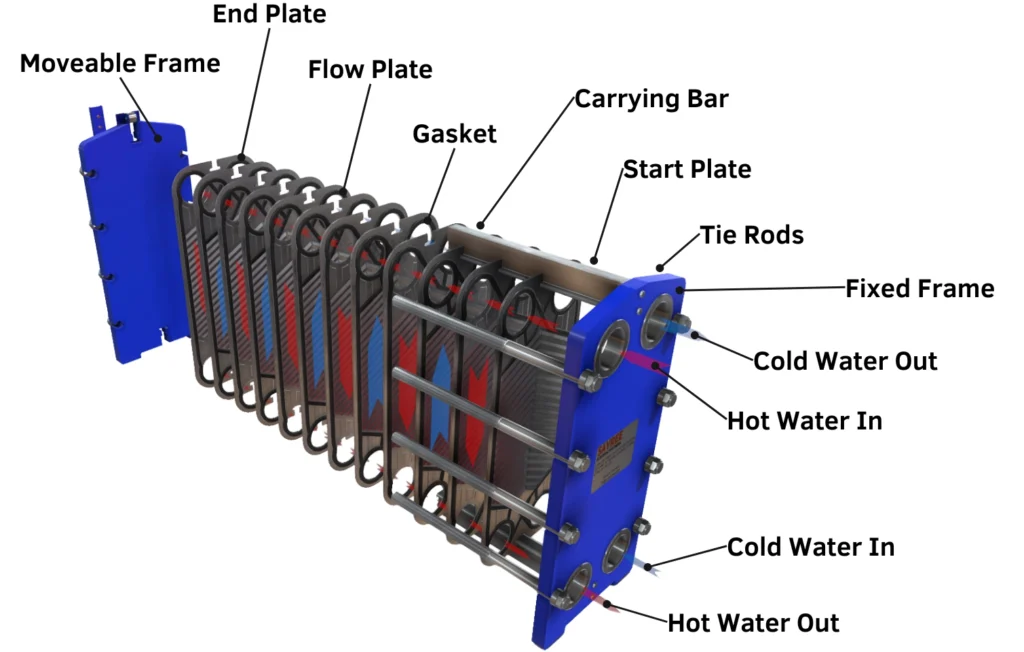
Plate heat exchangers are critical in industries requiring efficient heat transfer between fluids. In HVAC systems, they provide energy efficiency through temperature regulation. The chemical industry uses them for process heating and cooling, supporting reactions and maintaining stability. In food and beverage, they manage pasteurization and chilling processes, ensuring product safety. Refrigeration systems also benefit from their compact design and efficient heat distribution. The ability to handle varying pressures and temperatures makes plate heat exchangers invaluable for any industry needing robust thermal management solutions.
Conclusion
Heat sinks play a pivotal role in diverse industries by ensuring device efficiency and safety through effective heat management.